1. What is a Blockchain?
A Blockchain, originally block chain, is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography.

Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
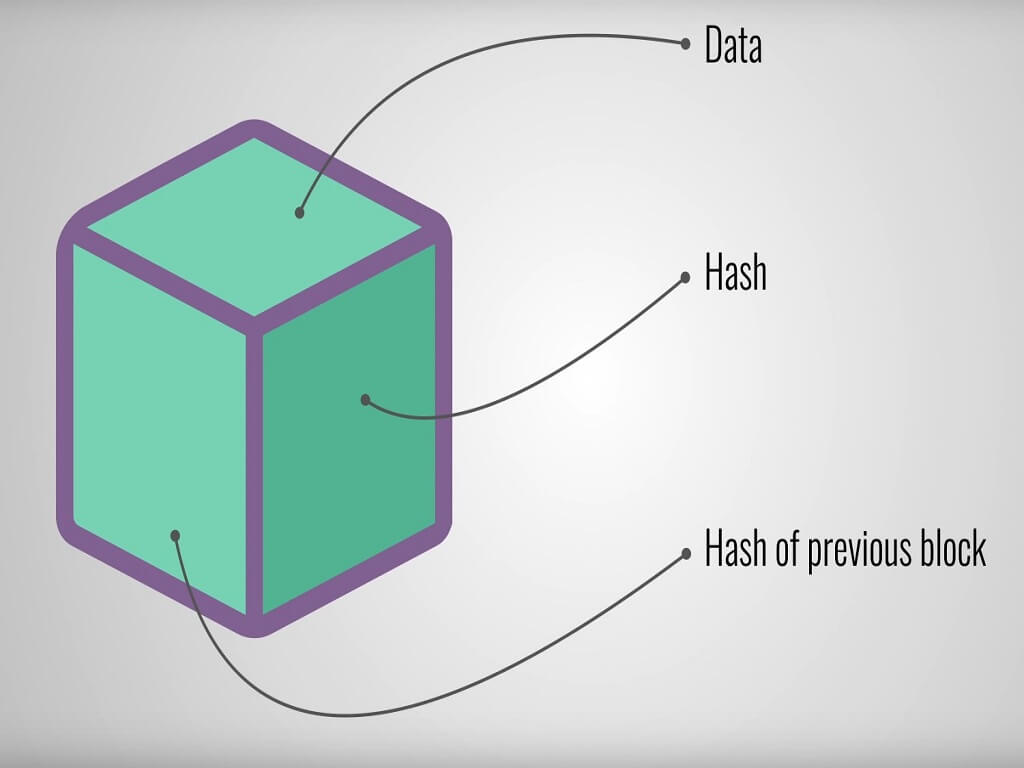
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is "an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way".

For use as a distributed ledger, a blockchain is typically managed by a P2P (peer-to-peer) network collectively adhering to a protocol for inter-node communication and validating new blocks.
Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority. Although blockchain records are not unalterable, blockchains may be considered secure by design.
2. How it is different from other technologies?
The blockchain is centralized. While all records secured on a blockchain are centralized, each participant on a blockchain has a secured copy of all records and all changes so each user can view the provenance of the data.
The data can automatically identify and correct itself based on coded business logic (smart contracts) and consensus, participants are intrinsically able to trust it.
3. Is it really secured?
NO, there are multiple different attacks which have been performed on the blockchain where most of them were succeeded. Though many multiple security mechanisms were introduced to make blockchain more secured, attacker’s come up with new attacks every day.